All You Need to Know About the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in your joints. Here is everything you need to know about the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
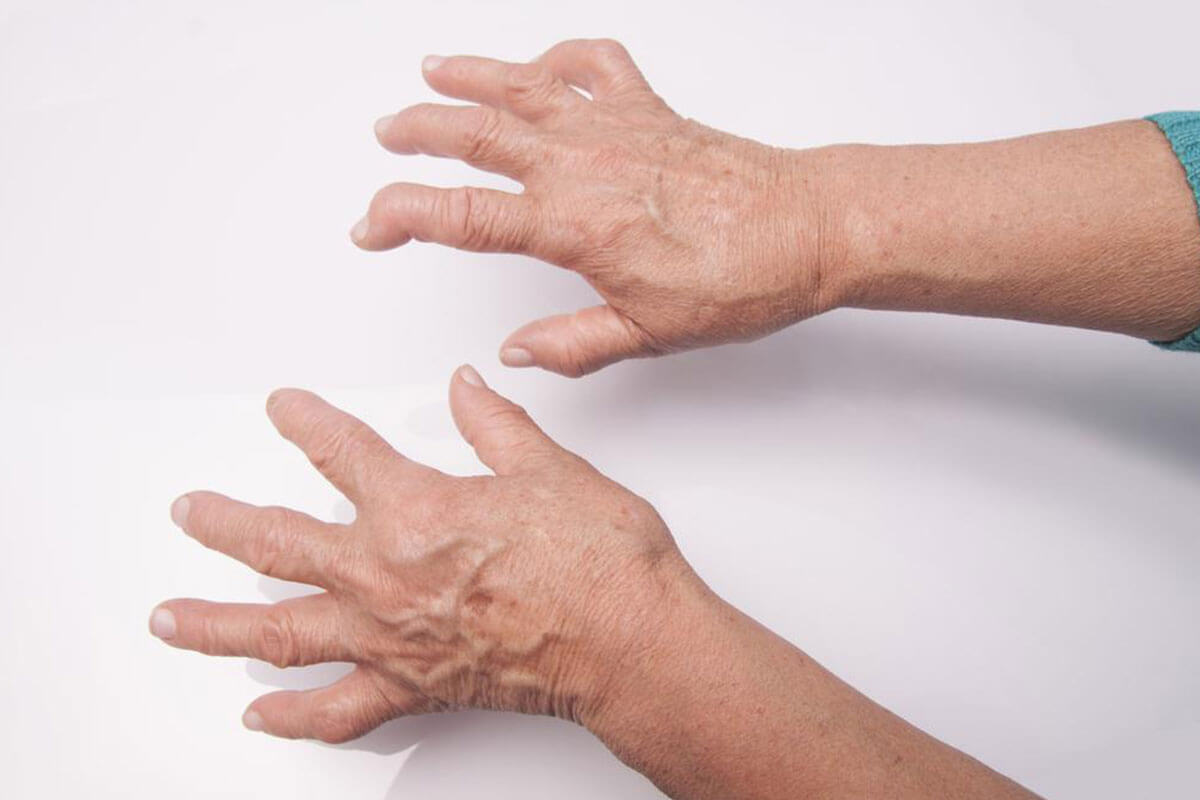
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in your joints, usually, the small joints of your hands and feet. Affecting around 1.5 million people in America, this form of arthritis can lead to cartilage damage, if it is left unchecked. It is much more common in women and generally occurs in individuals over the age of 40. Apart from affecting the joints, rheumatoid arthritis can also cause problems in other organs of the body like the eyes, blood vessels, skin, and the lungs.
Fatigue, fever, morning joint stiffness, swollen and tender joints, and weight loss are some of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. In most cases of this type of arthritis, the symptoms are symmetrical. In other words, most often than not, the same joints are affected on both sides of the body. The rheumatoid arthritis symptoms vary in severity from one person to another. They also tend to come and go; the periods of the symptoms flaring up will alternate with periods when the symptoms go into remission. Over a period of time, as this disease progresses, it can cause the joints to shift out of place and deform.
No known cause of rheumatoid arthritis has been found yet, therefore, the treatment plan basically focuses on easing the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis and the discomfort caused due to joint stiffness. The treatment plan can only go into action after the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is made.
It can be quite difficult to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis because there are many conditions that cause joint inflammation and joint stiffness. Also, there is no single definitive test for this type of arthritis. The doctors, typically, conduct a physical exam first to check for the joint symptoms like swelling, warmth, and redness. Along with the examination of the joints, they will also check your muscle strength as well as your reflexes. Once the doctor suspects arthritis, you may be asked to undergo certain blood tests or joint imaging test to confirm the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. The tests that are used for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis are:
- Blood Tests
There is no single blood test that can either rule out or prove a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. However, there are some blood tests that can point out the possible indications of this disease. They are:
- C-reactive Protein (CRP)
C-reactive protein is a substance that is produced by your liver in response to any inflammation in the body. The CRP test is a blood test that only indicates whether there is inflammation in the body by measuring the amount of CRP in your blood. If the count of CRP is really high, it indicates that you are suffering from inflammation. However, this does not anyway confirm the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rheumatoid Factor test
This is one of the specific tests that can help in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, however, it is not always accurate. It is true that rheumatoid factor is present in more than half the people who are suffering from this condition. But sometimes, a person who does not have RA also tests positive for this factor.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Complete blood count is done for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis to check whether you have anemia, which is a condition where there is a lack of red blood cells. People suffering from rheumatoid arthritis tend to have anemia, but this does not mean that having anemia is a sign of RA.
- Joint Imaging Tests
There are several joint imaging tests that can be performed for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis to check for joint damage and inflammation. These imaging tests also help doctors distinguish between the various types of arthritis. Sometimes, doctors use these tests to monitor the progression of this disease. Some of the scans that are used in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis are:
- Ultrasound scans – These scans make use of high frequency sound waves to produce the image of the affected joints.
- X-Rays – Scans that use radiation to examine your joints are called x-rays.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – If the goal is to generate detailed images of the joints, MRI scans are taken. These scans make use of strong radio waves and magnetic field to create the image.
These are the most commonly used tests for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.



