Diseases & Conditions
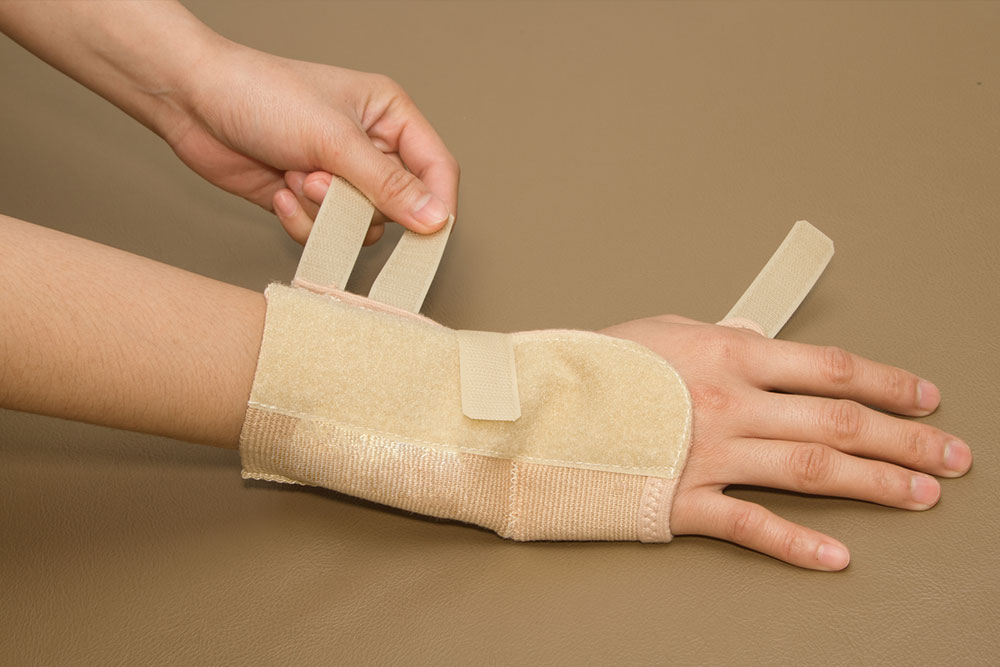
A Brief Overview of Wrist Braces and Its Types
When you feel pain or numbness in the fingers, it could be indicative of carpal tunnel syndrome. Well, it is a common type of condition that generally occurs in people working in various fields. This condition occurs when you put too much pressure on the median nerve. The median nerve is the nerve of your body that provides sensory signals to all your fingers except the little finger. In some cases, carpal tunnel syndrome will go away with time with the use of some types of wrist braces. However, there are certain cases in which the condition could persist and the patient might require surgery. In this article, a brief overview of a wrist brace and its types have been given. It aims to provide essential information on how a wrist brace can help you. What are wrist braces? A wrist brace is a type of garment that is generally worn in order to protect the wrist of people who are suffering from wrist pain or any type of pain in the area. It provides strong protection around your wrist which allows the condition to heal effectively. It is a very common rehabilitation method for those who have a wrist injury.