Tips
What Causes Body Odor and How to Prevent it
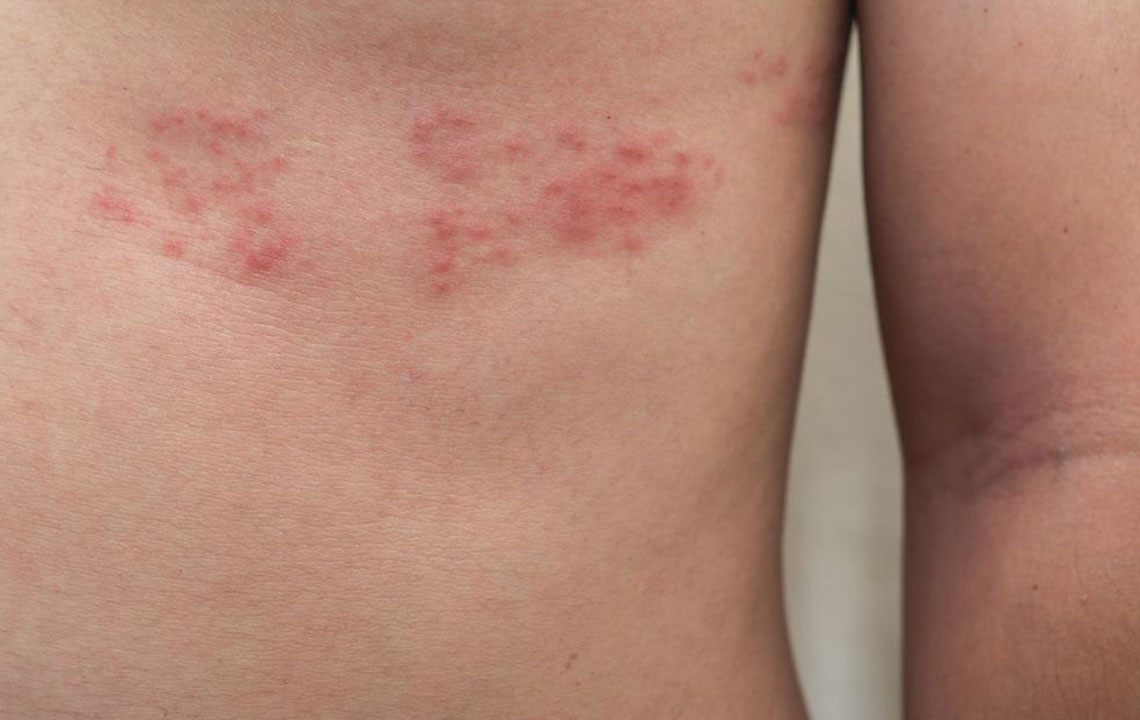
Smelling bad can be embarrassing, and you’ll put the people around you in an awkward position. While mild body odor is something all of us experience, constant body odor, and too much of it, is not a good thing. What are the causes of body odor? While not having a bath regularly is one of the most basic reasons, there are a few other underlying causes that might contribute to the bad odor as well. Excess consumption of spicy foods Been indulging in too much spicy food? Your extra spicy street food and dishes could be one of the causal factors of body odor. You are what you eat. While this is an arguable statement, it does have a grain of truth to it. The spice you eat, when broken down, causes your body to release gases that contain sulfur. These sulfur gases are released through the pores of your skin, the smell of body odor. Does that mean you should stop eating spice? Not at all. Just lower the intake of spice, drink plenty of water through the day especially after a spicy meal, and avoid spicy foods the day before a party or date. A hot shower and deodorant can help too.