Health
Key details to know about acute graft versus host disease
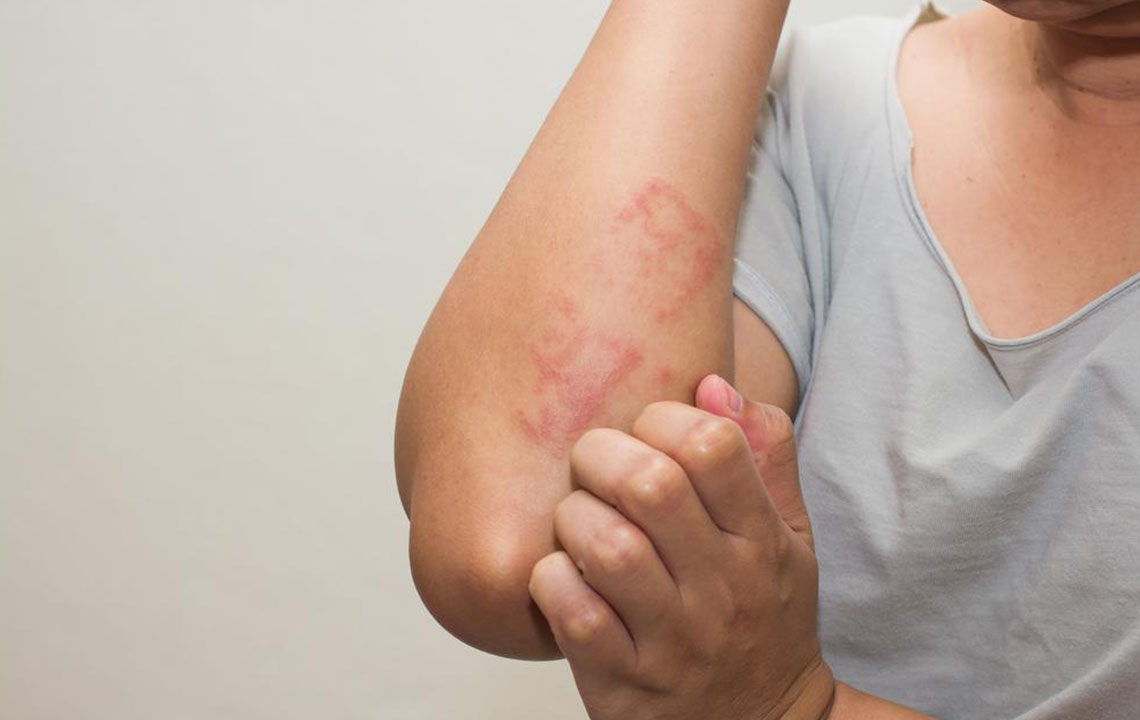
During an allogeneic transplant, a healthcare expert introduces hematopoietic stem cells from a donor into the host’s body. These donated stem cells eventually turn into mature blood cells. However, in some cases, the donated cells may perceive the host cells as a foreign threat, attacking the recipient’s cells as an immune response. This condition is known as graft versus host disease (GvHD) and can develop into two types, including acute graft versus host disease (aGvHD). Occurrence Healthcare professionals used to classify GvHD based on the timing of the symptom onset. Nowadays, providers diagnose specific types of GvHD based on symptoms and healthcare trials, in addition to the onset of symptoms. Acute graft versus host disease (aGvHD) typically develops shortly after a transplant, usually within the first 100 days. However, the symptoms of this type may appear at a later stage. Another commonly seen type is chronic graft versus host disease (cGvHD), which might develop any time following an allogeneic transplant, with a majority of the cases starting within two years. Symptoms The symptoms of aGvHD can range from mild to moderate to severe, typically affecting the skin, liver, or gastrointestinal tract (GI). Affected persons may also experience a range of symptoms, including a rash or reddened areas on the skin accompanied by itching or pain.